|
|
Information Lifecycle Management – Addresses Information Explosion
by N. Santosh Kumar, Student MBA(IT), 1st Year, IIIT Allahabad
The information explosion is everywhere. Today the information is growing faster than the decline in prices. Estimates indicate information stored on computer systems is growing by more than 100 percent per year, and the cost of managing storage is rising to more than 90 percent of the acquisition cost. Industry experts believe that storage utilization rates are running only 40 to 60 percent, which means that nearly half of every dollar spent on storage may be wasted. Information can no longer exist in storage silos or one dimensional life cycle. As a result there is a need for a strategic system to effectively manage the growing volumes of information from creation to disposal according to its changing value to the business. Information Lifecycle Management is for it.
“Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) is comprised of the policies, processes, practices, and tools used to align the business value of information with the most appropriate and cost-effective IT infrastructure from the time information is conceived through its final disposition. Information is aligned with business requirements through management policies and service levels associated with applications, metadata, and data.”
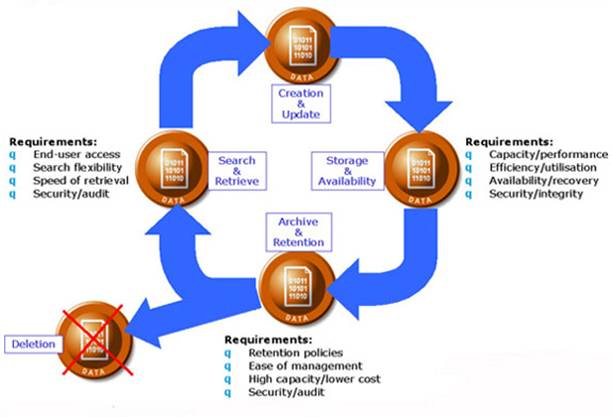
Or – To put it in simple.
Information Lifecycle Management is a business analysis of the trade-offs between cost and availability. The primary storage solutions are the most expensive per megabyte, but they also offer the greatest availability. Information Lifecycle Management is a process whereby the business determines how to invest in its information storage budget.
In every organizations information is the critical part. But most of the time the information collected is just left as data or they are difficult to access as time passes. The data are not put to use according to the wants in business. Today's urgent e-mail is more important than last year's staff memo. Over time, the value of information keeps increasing or decreasing. ILM lets you access and mine information to enrich and streamline business processes, identify new revenue opportunities, and remain competitive. Its need is increasing for the better competitive stand. In The Info Pro's(TIP) "Technology Heat Index," which ranks various technologies by users' purchasing plans, ILM moved from the number-four position in TIP's April 2005 survey to the number-one spot in the most recent survey. Leading companies such as IBM, EMC, Storage Technology, Sun Microsystems, Veritas Software, Computer Associates, Oracle, Network Appliance, Engenio Information Technologies, and Hitachi Data Systems are working on the strategic implementation of ILM.
ILM can be very effective for the ERP systems. The information is prioritized and stored accordingly for the better performance of the system. This can give the competitive advantage for the tough competition. With the proper implementation of ILM with ERP systems the Decision Support Systems can give the best possible results.
Essential Steps for Developing an ILM Strategy
ILM is not simply a matter of placing data on the most appropriate, cost-effective storage media during its lifecycle. About 25 percent of the challenge is about the selection of products. The key for getting it right is in implementing the right business processes and supporting them with the right tools. Data must be stored based on the objectives of the business. The value of the data and how the data is used can--and likely will--change over time is the key for implementation. An effective ILM solution is composed of an interconnected set of business processes, storage components, and data and storage management applications.
ILM is not something you buy off the shelf. A number of steps are critical to developing a successful ILM strategy and it should involve a variety of stakeholders--from IT and business decision-makers to compliance officers and executive sponsors. Here are the typical steps to developing an ILM strategy. Each of these phases reflects the fact that data's role changes over time:
- Analysis of requirements of data, business and regulatory inventory.
- Solution design (capacity and performance planning, hardware selection, network integration).
- Security audit.
- Document retention policies.
- Chain of custody.
- Auditing.
- Billing and charge-back.
- Backup and disaster recovery.
- Customization.
A better managed information flow is the need of the hour. No doubt the information keeps growing but mismanaged storage and unnecessary spending on it costs a lot to organizations. Properly implemented ILM gives solutions to these problems.