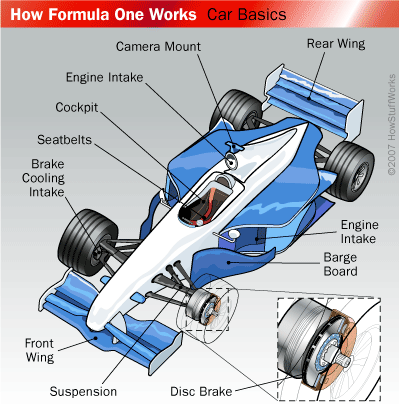
Construction
of Formula 1 Racing Car
A formula 1 car is a jet fighter as it does with an
ordinary road car. Its aerodynamics features have become a key to success in
the sport and teams spend millions of dollars on research and development.
Step 1: Cutting
An ultrasonic cutting machine is used to
measured sheets of resin-impregnated carbon fiber cloth. This machine is
computer controlled and the cutting fiber has to be stored at 18 degree
centigrade.

Step 2:
Molding
This cutting
sheet laid into molds patters in a special air-conditioned clean room .The
material is then put in a vacuum bag.
Step 3: Autoclave
They are moved to the autoclave. A sealed
vessel that applies pressure between 2 and 6 times normal atmospheric
pressure. The pressure, combined with
the vacuum bag, ensures that components fit the molds exactly, while the heat
(usually between 130 and 140°C) hardens the resin.
Step 4: Assembly
The parts are sent to the assembly and this
ensures that all parts can fit together properly. If drilling or other
machining is required, the parts are sent back to the CNC division.

Engine
Technology
Only two other F1 teams (Ferrari &
Renault) constructs both its own engines and chassis. The close coordination
between these two technical departments confers an advantage because it enables
Panasonic Toyota Racing's designers and engineers to envision the car as a
whole from the very first concept drawings. The word "drawing" is
something of a misnomer, since the engines and chassis are designed on
computers using CATIA CAD software. It takes around 1500 detailed
"drawings" to make a complete engine.

References
http://www.formula1.com/default.html