|
Solution to the case study posted in the previous
issue.
Nikita Bhargava.
(nbhargava_mba04@iiita.ac.in)
Summary of the problem:
Wayne Hills Hospital is a small, remote hospital in Wayne, Nebraska.
The case deals with its problem of stocking blood which is expensive and
has a limited shelf life.
Wayne hills want to keep its stock as low as possible to cut the expenses
and at the same time want to meet the contingencies. The hospital administrator
wants to set an 85% service level. The implications of this decision are
to be discussed.
Highlights of related issues:
Blood is a very important component of the human body. In cases of profuse
bleeding; we need blood immediately to recover the loss and to sustain
the blood level.
How to stock blood which is expensive, perishable and at the same time
mandatory; especially in a small remote hospital is the major issue. Another
issue is of the life saving drugs.
Implication of the decision taken by the administrator:
The health care environment of Wayne Hills appears to be an appropriate
arena for application of the value marketing chain concept.
The value marketing chain differs from the respected “value chain”
as described by Michael Porter in his classic work on business strategy.
Competitive Advantage value chain consisted of the linked set of functions
or processes that enable businesses to deliver superior value to customers
and thereby achieve superior performance. The process starts with “inbound
logistics” then continues “outbound logistics” to attract
customers and service to keep them happy.
Thus apart from good service from efficient doctors, good logistics of
blood, drugs etc may give the competitive advantage that Wayne Hills need
and keep its patients happy. It is a remote and a small hospital; its
competitive edge might attract faraway patients too and generate revenues.
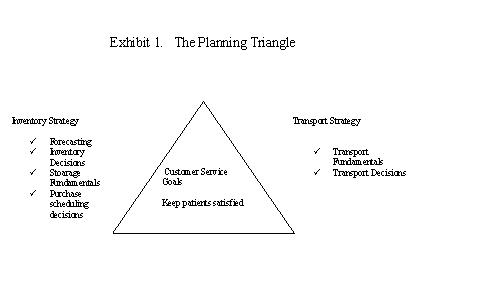
Alternate solutions and answers to the questions that follow:
I have used the planning triangle (Exhibit 1) for providing
the solution to an effective logistics strategy for blood and drugs and
have also tried to answer the questions that follow through it.
Inventory Strategy
To develop an effective inventory strategy and for making forecasting
decisions, we can make a Hospital Resource Information System
(HRIS).The HRIS would keep a record of patients history such
as sex, age, drugs consumed, medical history, time, whether blood transfusion
was required and if yes ,its group ,RH factors and so on.
According to the WHO ruling, only authorized blood banks recognized by
the Government(which fulfill the parameters needed) can stock blood and
do cross matching*.
A note on cross matching
Blood can be broadly classified into four groups namely O, A, AB and
B and then into subgroups with RH +ve and RH -ve factors.
Keeping a stock of all varieties is tedious and cumbersome.
Cross matching is the matching of the patient’s sample blood group,
RH factor etc with the donor’s blood group, RH factor and checking
for no untoward reactions.
If the match exists and the donor’s blood is tested against blood
borne diseases like AIDS, HEPATITIS and other venereal diseases, then
the blood can be infused into the patient’s body. Since it is such
a tedious process, setting up the infrastructure for a blood bank and
fulfilling the formalities may be very costly for a tiny hospital like
Wayne Hills; the strategy proposed is that of outsourcing.
Wayne hills should not stock any blood with itself; rather take it from
the blood bank as and when needed.
The hospital can have tie-ups with a blood bank based on location, distance
and capacity.
The blood banks can also develop a blood bank information system
(BBIS).The BBIS will have all information about the donors; the
donor list, blood group, RH factors, date, time of donation and so on.
Apart from purchase basis, the blood procurement could be on the exchange
basis from the family members of the patient.
The BBIS is integrated with the HRIS for effienciency and responsiveness.
How it all works?
As soon as a patient comes who require a blood transfusion , his entry
would be made in the HRIS and an availability check would immediately
be made into the BBIS and the patient’s sample sent to the blood
bank for cross matching.
The transportation could be through a courier by air or rail with proper
temperature conditions and care ensured.
For immediate treatment and prevention of hypovolumic shocks in cases
of profuse bleeding, Wayne Hills could provide substitutes like Intravenous
Fluids (IV Fluids), Haemaecal (which is a synthetic substitute of plasma
to expand the plasma), Ringer’s Lactate solution which is full of
ions for sustainability till cross matching is done.
The hospital can only stock the blood of the patients being treated
in the hospital and the rest being dependent on blood banks.
Now arises the question of life saving drugs. We know that 85% service
level is to be maintained. For this again, from the accumulated data in
HRIS, we can get answers to questions like:
a) How many beds are there in the hospital?
b) How many patients need the life saving drugs?
c) Consumption was heavy in which months or particular seasons….For
example in rainy seasons, accidents may be more and so on.
Based on this information we will have an idea of which drugs are needed
more.
For e.g. Life saving drugs like steroids e.g. Decadron, Vasopressures
(to increase blood pressure) e.g. Mephytain, Anti Histaminic injections
e.g. Anvil may be needed more than Andrlalin and Non Andralins.
In other words, we can exercise management by exception;
categorize them and perform an ABC Analysis based on
its criticality, non availability etc.
Exhibit II: ABC Analysis
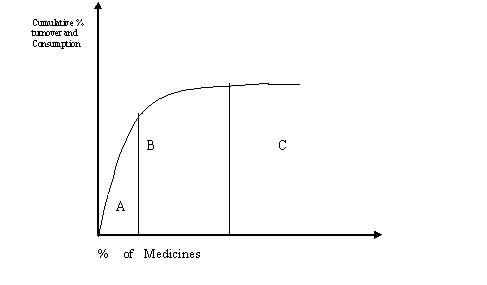
In addition to the above; we can perform a VED (Vital, Essential,
Desired) Analysis.
In the vital ‘V’ we put medicines having extreme criticality.
In desirable ‘D’ we will put those that are desirable but
not critical and finally in ‘E’ we will be putting those that
lie in between.
Thus for purchasing decision we can perform an ABC-VED Matrix
classification .This classification needs to be monitored periodically
and changes need to be incorporated accordingly. For instance, a disease
may be completely eradicated and its medicine may no longer be needed
Again we can go for a forward buying or a hand
to mouth purchasing decision based on the matrix classification.
The purchases should try to take advantages of Quantity Discounts
and Dollar Averaging.
Wayne Hills being a small hospital, a second issue could be of obsolesce
and expiry in case of medicines. Thus the purchasing department should
be vigilant enough to have tie ups with company suppliers to return those
medicines which are to be expired in a few months in exchange of others.
The company may push those medicines into bigger hospitals where there
is a larger demand. Hence here good supplier relations are crucial.
A last word:
The hospital should also incorporate a measurement scale for service
quality known as SERVQUAL- instrument developed by PZB in 1988.
It would tell us further gaps and steps can be taken to narrow these gaps.
References:
1. www.google.com
2. Supply Chain Management by Chopra n Mendel.
3. Global Operations and Logistics by Dornier, Ernst, Fender, Kouvelis.
4. Chit chats with a few doctor friends.
|

