INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (ISMS)
By:
Rahul -MSCLIS Semester-II
Indian Institute of information Technology-Allahabad
Introduction
Information assets are significantly important to any business process and crucial to the survival of any organization in today’s digitalized economy. In this era of immense corporate competitions and as the concept of globalization is gaining momentum leads to dependency on information processing facilities.
However, the question arises Information like any other asset to an organization is a valuable asset and if lost can interrupt the business so it needs to be suitably protected.
Any organization has wide range of information with it, like papers (printed or written) databases, Films, Tapes, Conversation etc. and if it is not well protected it can be leaked, disclosed in an unauthorized way, can be modified thus decreasing its value, and will become unavailable when needed. Therefore, there is need of an information security system in an organization to avoid this unwanted situation.
Hence protecting information is a daunting challenge which can be achieved by implementation of ISMS which is a well through approach which addresses the organizational issues of information security so that C, I, A (Confidentiality Integrity Availability) of information remains intact. ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that provides establishment of organizational wide information security management system for the security of organizational most valuable information assets. This standard is considered as Best Security Practices which lowers down the risk of any security incident.
Business requirements for ISMS.
What are the business requirements that force any organization to implement ISMS? The requirement can be categorized in two main heads:
- Commercial requirement
- Legal requirement
Commercial requirement : Commercial requirement may come from the side of Client or Stakeholders. Some times for marketing its service any organization go for ISMS and some time it is implemented to demonstrate to the trading partner the commitment to information security.
Legal Requirements : Legal requirements may come from Trading regulation, IPR regulation, Information protection requirements etc.
Why does any organization need to protect its business information?
Any organization can have information which is important for effective and uninterrupted business flow and to keep alive their goodwill in this competitive market.
ISO and IEC
ISO is the International Organization for Standardization. It was established in 1947 and is located in Geneva, Switzerland. Its main objective is to develop standards that support and facilitate international trade. IEC is the International Electrotechnical Commission was set up in 1906 and is located in Geneva, Switzerland. Its function is to develop standards for all types of electrotechnologies. Nationalized member bodies support both ISO and IEC. Moreover, these members participate in the standards improvement process through technological committee.
ISO IEC 27001
ISO IEC 27001:2005 was developed by ISO/IEC JTC 1, SC 27 ( Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 27). JTC 1 is responsible for all kinds of information technology standard while SC 27 is specifically responsible for the development of standards related to IT security techniques.
ISO IEC 27001: 2005 officially published on October 15, 2005 cancels and replaces the old BS 7799-2 standard (published in 2002 by BSI). The old BS 7799-2 information security standard has become obsolete and is no more in practice officially.
There are various methodologies to implement ISO 27001 but most of the organization uses the business risk approach because this methodology is used keeping in view the various business risk to which an organization is exposed to
Business risk methodology problem solving process:
In order to demonstrate the ISO 27001 implementation we have taken the IT environment industry as a platform. The whole ISO 27001 implementation undergoes through various phases and these phases can be categorized in basically in four phases viz. Plan, Do, Check, Act or PDCA which is also known as Damming wheel and in this report we have dealt with each phase and processes involved in the same.
PLAN (Establish ISMS)
This is the first phase of the PDCA model for the ISMS implementation and in this phase we establish ISMS policy and define its scope. It consists of the objective of the policy as well as the procedures, processes and controls followed for the managing the risk and improving the information security to achieve the aims and objectives of the organization in a time sensitive period. This stage includes.
- Gap Analysis
- Risk Assessment
- Information Security Policy
- Statement of Applicability
PDCA Cycle (Damming wheel)
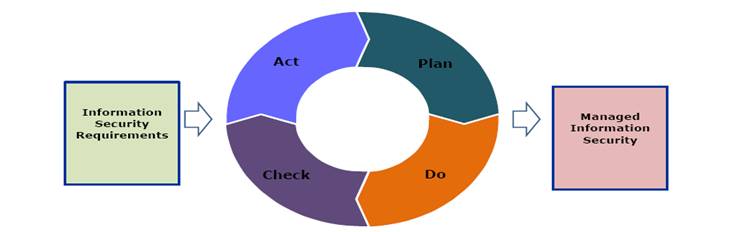
DO (Implement and operate ISMS)
This is the second stage of the PDCA model; here we mainly concerned with the implementation of ISMS policy its objectives, processes, procedures and controls. A risk treatment plan is formulated for the effective implementation of ISMS. For the effective implementation of ISMS, process training programme has been conducted for the employees of the concerned organization. This stage includes.
- Risks Treatment plan -IS Standards & Procedures
- ISMS Controls Implementation, Process definition and documentation.
- Process Trainings & Awareness
- Incident Management
- Business Continuity plan.
CHECK (Monitor and review ISMS)
Check phase is the most significant part of the PDCA model. In this stage we check the effectiveness of ISMS policy, here we try to know whether implemented controls are good one to achieve the objectives of the ISMS or not. If any non-conformities has been found then it has been reported to management for their reviews. If it is needed in the check phase that certain controls are need to be implemented again then the same one is repeated. Check phase covers the following steps:
- Check point reviews
- Internal Audits.
- Management review
ACT (Maintain and improve ISMS)
This is the last phase of the PDCA model. In this stage the corrective and preventive action has been taken to resolve the major and minor conformities found in the check phase during the internal audit, so that consistent ISMS improvement may take place. Here in this phase we follow the following steps:
- Non-Conformities Identification.
- Plan and implement measures.